
While doing this, the response of the pupil of both eyes is observed. While you are looking at a distant object, the examiner will briefly direct the beam of a small flashlight at one of your eyes a few times. Typically, pupil testing is performed in a dimly lit room.
#Star pupil definition professional
Pupil Testingĭuring a routine eye exam, your eye care professional will inspect your pupils and test your pupillary function. This is called the accommodative pupillary response. In addition to being affected by light, both pupils normally constrict when you focus on a near object. Generally, normal pupil size in adults ranges from 2 to 4 millimeters in diameter in bright light and 4 to 8 millimeters in the dark. Also, pupil size changes with age - children and young adults tend to have large pupils, and seniors usually have small pupils. The size of the pupil varies from person to person. In bright conditions, the pupil constricts to limit how much light enters the eye because too much light can cause glare and discomfort, and may even damage the lens and retina. In low-light conditions, the pupil dilates so more light can reach the retina to improve night vision. This dynamic process of muscle action within the iris controls how much light enters The size of the pupil is controlled by muscles within the iris - one muscle constricts the pupil opening (makes it smaller), and another dilates the pupil (makes it larger). Using the analogy of a camera, the pupil is the aperture of the eye and the iris is the diaphragm that controls the size of the aperture. Together, the iris and pupil control how much light enters the eye. This is due to the intense light from the flash being reflected by the red colour of the retina. Depending on the direction of your gaze when the photo is taken, your pupils might appear bright red. There's another common situation when the pupil of the eye changes color - when someone takes your photo using the camera's flash function.
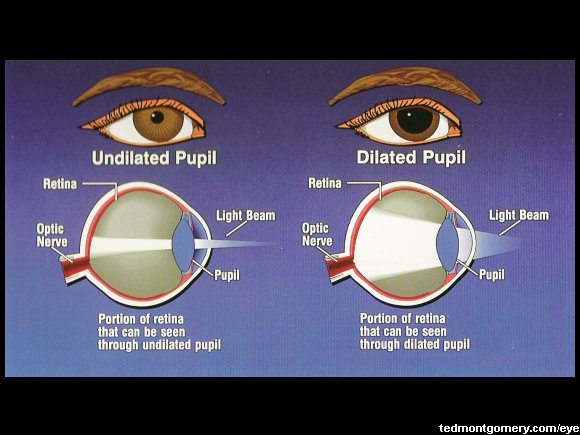
When the cloudy lens is replaced by a clear intraocular lens (IOL) during cataract surgery, the normal black appearance of the pupil is restored. If the pupil has a cloudy or pale colour, this is typically because the lens of the eye (which is located directly behind the pupil) has become opaque due to the formation of a cataract. The black colour is because light that passes through the pupil is absorbed by the retina and is not reflected back (in normal lighting). Typically, the pupils appear perfectly round, equal in size and black in colour.
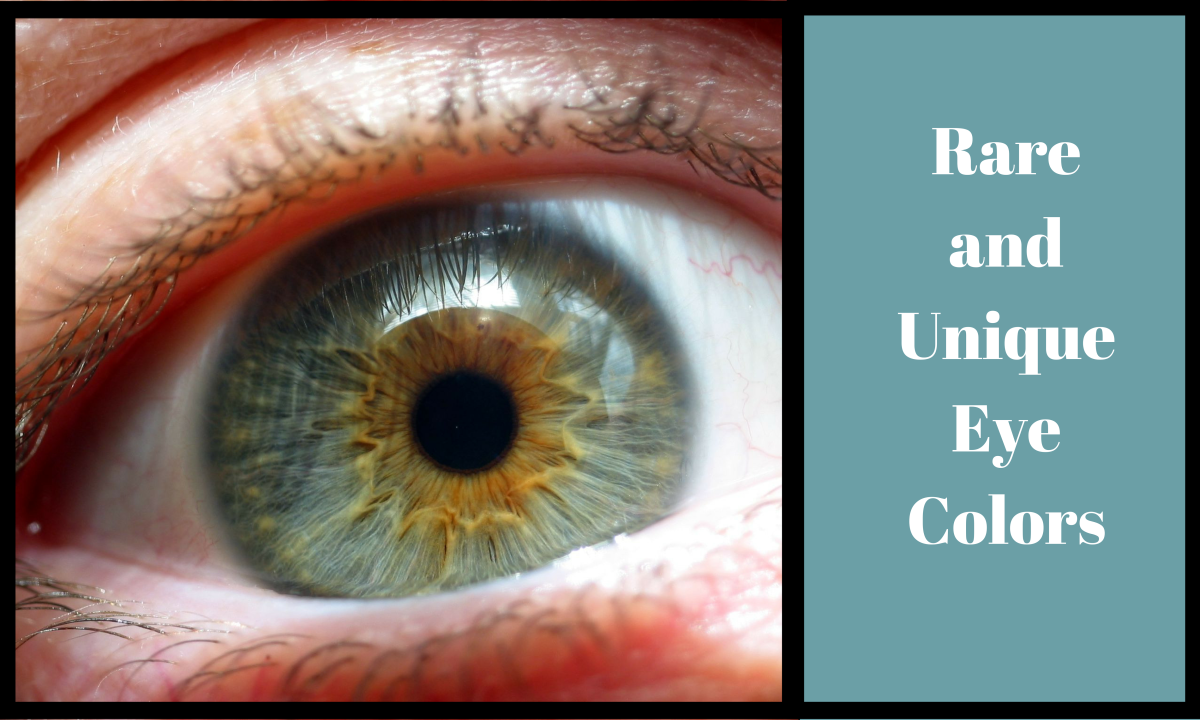
The function of the pupil is to allow light to enter the eye so it can be focused on the retina to begin the process of sight. The pupil is the opening in the centre of the iris (the structure that gives our eyes their colour). One of the most important parts of the eye isn't a structure at all - it's an open space.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
